Reference : C# 입문부터 안드로이드, 윈도우 앱(UWP) 동시에 만들기 Xamarin Forms(자마린 폼즈) + Maui(마우이)
학습 페이지
www.inflearn.com
< 클래스 생성자 오버로딩 >
클래스 생성자:
클래스를 생성할때 호출되는 메소드로 클래스 이름과 같다.
생성자는 다른 메소드 처럼 반환값을 가질 수가 없다.
오버로딩:
함수의 이름은 같고 매개변수를 다르게 하여 개발하는 방식
public class Rectangle
{
public int Width { get; set; }
public int Height { get; set; }
// Default constructor
public Rectangle()
{
Width = 0;
Height = 0;
}
// Constructor overloading
public Rectangle(int side)
{
Width = Height = side;
}
public Rectangle(int width, int height)
{
Width = width;
Height = height;
}
}이 것을 다른 .cs에 있다고 가정 했을 때,
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp2
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
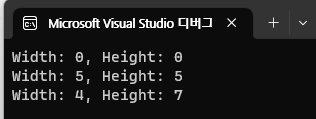
Rectangle r1 = new Rectangle();
Console.WriteLine($"Width: {r1.Width}, Height: {r1.Height}");
Rectangle r2 = new Rectangle(5);
Console.WriteLine($"Width: {r2.Width}, Height: {r2.Height}");
Rectangle r3 = new Rectangle(4, 7);
Console.WriteLine($"Width: {r3.Width}, Height: {r3.Height}");
}
}
}.Height,.Width로 가져올 수 있다.
< 상속과 Protected >
C#에서 상속을 사용하면 한 클래스가 다른 클래스의 속성과 메소드를 상속 받을 수 있다. protected 접근 한정자는 해당 클래스 및 상속받은 클래스에서만 접근이 가능하게 한다.
상속:
다른 클래스에 정의된 멤버를 불려 받을 수 있는 기능
상속해주는 클래스 - 부모클래스
상속 받는 클래스 - 자식클래스
public class Animal
{
protected int legs = 4; // protected 변수
public void Eat()
{
Console.WriteLine("Eating...");
}
}
public class Dog : Animal // Animal 클래스를 상속 받음
{
public void Bark()
{
Console.WriteLine($"Barking with {legs} legs..."); // protected 변수 사용
}
}class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Dog dog = new Dog();
dog.Eat();
dog.Bark();
}
}
< Sealed 클래스와 메소드 오버라이딩 >
C#에서 'sealed' 키워드는 클래스를 봉인하여 다른 클래스가 해당 클래스를 상속받는 것을 막는다.
즉, 클래스명 앞에 sealed를 붙이면 상속을 못 하고 인스턴스화를 해서만 사용할 수 있다.
오버라이딩 (Overriding) :
오버로딩과 비슷하지만 오버로딩은 클래스내에서 동일한 이름으로 매개변수를
다르게 하는 방식이고 오버라이딩은 클래스의 상속관계에서 메소드를 재정의 하는 방법
sealed class SealedClass
{
public int x;
public int y;
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
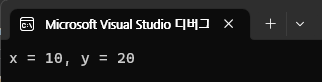
SealedClass sc = new SealedClass();
sc.x = 10;
sc.y = 20;
Console.WriteLine($"x = {sc.x}, y = {sc.y}");
}
}
메소드 오버라이딩
C#에서 메소드 오버라이딩은 상속받은 메소드를 자식 클래스에서 재정의하는 것을 의미한다. 이를 위해서는 기본 클래스의 메소드에 virtual 키워드를 사용하고, 파생 클래스에서는 override 키워드를 사용해야 한다.
public class Animal
{
public virtual void sound()
{
Console.WriteLine("This is the sound of an animal");
}
}
public class Dog : Animal
{
public override void sound()
{
Console.WriteLine("This is the sound of a dog");
}
}class Program
{
static void Main()
{
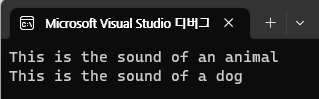
Animal myAnimal = new Animal();
Animal myDog = new Dog();
myAnimal.sound();
myDog.sound();
}
}
< Partial 클래스 >
파샬 partial class :
두개 이상의 파일이 클래스를 나뉘어서 개밝하는 방식
컴파일시 자동으로 결합이 되고, 코드가 길어질 경우 관리를 수월하게 할 수가 있고,
하나의 클래스를 여러명에서 동시에 작성할 수 있다.
partial class 클래스명
{
//코드
}
// File1.cs
public partial class PartialClass
{
public void Method1()
{
Console.WriteLine("Method 1");
}
}// File2.cs
public partial class PartialClass
{
public void Method2()
{
Console.WriteLine("Method 2");
}
}class Program
{
static void Main()
{
PartialClass myClass = new PartialClass();
myClass.Method1();
myClass.Method2();
}
}
< 추상 클래스 >
C#에서 추상 클래스(abstract class)는 인스턴스를 만들 수 없고, 하나 이상의 추상 메서드(정의되지 않은 메서드, 즉 프로토타입만 있는 메서드)를 가질 수 있는 클래스를 말한다. 이 클래스는 반드시 상속을 통해 사용되며, 상속받은 클래스에서 추상 메서드를 구현(override)해야 한다.
abstract 추상클래스:
상속을 해주기 위한 클래스
abstract class 추상클래스
{
abstract public void message(); //상속받은 클래스에서 기능 구현
}
class 자식클래스 : 추상클래스
{
public override void message()
{
Console.WriteLine(“코드구현”);
}
}예를 들어서 동물소리를 추상메서드로 사용한다고 가정해보자.
public abstract class Animal
{
public abstract void animalSound(); // 추상 메서드
public void sleep()
{
Console.WriteLine("Zzz");
}
}이젠 돼지가 Animal을 오버라이드하여 구현하면 된다.
public class Pig : Animal
{
public override void animalSound() // 추상 메서드를 오버라이드하여 구현
{
Console.WriteLine("The pig says: wee wee");
}
}class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Pig myPig = new Pig();
myPig.animalSound();
myPig.sleep();
}
}
< 정적 Static 클래스 >
static 정적 클래스 :
인스턴스를 만들어서 사용할 수 없다.
생성자를 포함할 수 없다.
어디서든 접근할 수 있다.
static class 클래스명
{
static public string name;
} public static class MyMathClass
{
public static int Square(int num)
{
return num * num;
}
} static void Main()
{
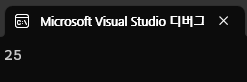
int result = MyMathClass.Square(5); // 인스턴스 생성 없이 사용
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
< 인터페이스와 네임스페이스 >
interface 인터페이스:
메소드 선언은 있지만, 기능을 구현하는 코드는 없다. 다중 상속을 위해 존재한다.
public interface 인터페이스명
{
void interfaceVoid();
}
public class 클래스명 : 인터페이스명
{
public void interfaceVoid()
{
//코드
}
}네임스페이스 namespace :
유효범위를 제공하는 선언,모든 식별자가 고유하도록 보장한다.
namespace ShapeNamespace
{
public interface IShape
{
double GetArea();
}
public class Rectangle : IShape
{
public double Length { get; set; }
public double Width { get; set; }
public double GetArea()
{
return Length * Width;
}
}
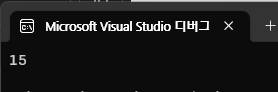
}파일을 별도로 분리하고 싶으면, Rectangle을 다른 파일에다가 옮겨도 똑같은 값이 나온다.
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle();
rectangle.Length = 5.0;
rectangle.Width = 3.0;
Console.WriteLine(rectangle.GetArea());
}
}
< 대리자와 익명 메소드 >
대리자 delegate:
매개변수와 반환형식을 갖는 메소드를 캡슐화 하며, 대리자는 참조하는 메소드의 메모리 주소를 가진다.
메소드를 보관하는 공간이고 필요할 때 이 공간을 가져와서 함수를 실행한다.
public delegate void MyDelegate(string msg);
class Program
{
public static void Hello(string strMessage)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello, " + strMessage);
}
public static void Goodbye(string strMessage)
{
Console.WriteLine("Goodbye, " + strMessage);
}
static void Main()
{
MyDelegate del = Hello;
del("Alice");
del = Goodbye;
del("Bob");
}
}
익명메소드:
별도의 메소드를 만들지 않고 불필요한 오버헤드를 줄일 수가 있다.
재사용할 필요가 없을 경우 사용한다.
public delegate void MyDelegate(string msg);
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
MyDelegate del = delegate(string name)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Hello, {name}");
};
del("Charlie");
}
}
< 이벤트 핸들러 >
C#에서 이벤트는 특정한 일이 일어날 때마다 호출되는 방법을 제공한다. 이벤트는 대리자를 사용하여 정의된다.
public delegate string MyDel(string str);
class EventProgram
{
event MyDel MyEvent;
public EventProgram()
{
this.MyEvent += new MyDel(this.WelcomeUser);
}
public string WelcomeUser(string username)
{
return "Welcome " + username;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
EventProgram obj1 = new EventProgram();
string result = obj1.MyEvent("Tutorials Point");
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
}
< 문자열 다루기 >
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
string txt = "Hello World";
Console.WriteLine("Length: " + txt.Length); // 문자열 길이 확인
Console.WriteLine("Upper: " + txt.ToUpper()); // 대문자로 변환
Console.WriteLine("Lower: " + txt.ToLower()); // 소문자로 변환
Console.WriteLine("Contains: " + txt.Contains("World")); // 특정 문자열 포함 여부 확인
Console.WriteLine("Index: " + txt.IndexOf("World")); // 특정 문자열의 위치 찾기
}
}
'C#' 카테고리의 다른 글
| C# 프로퍼티, 객체 초기화 (0) | 2023.06.08 |
|---|---|
| MS-SQL 및 SSMS 설치 방법 (0) | 2023.06.04 |
| C# 문법 정리 (0) | 2023.06.03 |
| C#으로 프로그램 만들기 (0) | 2023.06.02 |
| 비주얼 스튜디오 설치 및 환경설정 (For Windows) (0) | 2023.06.02 |